3 conversion mechanism
The conversion of the recyclate takes air as the oxidant, and the p-xylene oxidizes at 180-240° C. and 10-25 MPa to produce crude terephthalic acid. The cobalt and manganese ions in the mother liquor are recovered with oxalic acid to form oxalate precipitates. Cobalt oxalate and manganese oxalate precipitates are insoluble in water, but are easily dissolved in strong acids. They are heated in air at temperatures above 120°C to initiate oxidative decomposition. Therefore, the precipitate is recycled to the decomposition reaction in the paraxylene oxidation reactor to achieve the purpose of recycling the catalyst metal, reducing the amount of fresh catalyst, and reducing the production cost [5].
3 1 Conversion of Recyclate
With air as the oxidant, the p-xylene oxidizes to produce crude terephthalic acid at 180 to 240°C and 10 to 25 MPa. The cobalt and manganese ions in the mother liquor are recovered with oxalic acid to form oxalate precipitates. Cobalt oxalate and manganese oxalate precipitates are insoluble in water, but are easily dissolved in strong acids. They are heated in air at temperatures above 120°C to initiate oxidative decomposition. Therefore, the precipitate is recycled to the decomposition reaction in the paraxylene oxidation reactor to achieve the purpose of recycling the catalyst metal, reducing the amount of fresh catalyst, and reducing the production cost [5].
3.2 PX liquid-phase catalytic oxidation reaction mechanism
PX liquid-phase catalytic oxidation reaction uses cobalt acetate and manganese acetate as catalysts, bromide as accelerator and acetic acid as solvent to generate crude terephthalic acid. The reaction is a free radical oxidation reaction. There are many kinds of free radicals, peroxides, and metavalent metal ions in the reaction. At the same time, as the reaction progresses, water is continuously generated in the system, and these factors affect each other.
Loss of reactants and solvent consumption during PX oxidation. The oxidation of PX is a series of reactions in which there are a series of intermediate oxidation products, mainly para-methylbenzyl alcohol (TALC), para-tolualdehyde (TALD), p-toluic acid (PT acid), Carboxybenzaldehyde (4-CBA) and the like are generally considered to be oxidized to aldehyde groups and carboxyl groups in this order. Although a small amount of phthalaldehyde was found during the oxidation process, the amount of aromatic hydrocarbons generated by oxidation was very small. The reaction process was described in [6]. In this reaction, Co and Mn exist in the +2 and +3 states. Co3+ has an extremely high redox potential. Mn and Co have similar effects. They have a strong synergistic effect [7]; however, only metal ions are used. The catalytic PX oxidation has low selectivity and is more susceptible to decarboxylation reactions.
In order to improve the selectivity of the reaction, it is necessary to add an accelerator, bromine, to accelerate the reaction of aromatics and inhibit decarboxylation [5]. This process is accompanied by many side reactions, mainly the decarboxylation reaction of acetic acid and paraxylene oxidation process (about 60%). The main by-products are CO, CO2, CH4, etc., which are usually called the combustion of acetic acid.
In the process of decarboxylation of acetic acid, the ratio of n(Br-)/[n(Co2+)+n(Mn2+)] is very important. When the ratio is less than 10, the combustion of acetic acid can reach 10% after 90 minutes of reaction; and when n( When the ratio of Br-)/[n(Co2+)+n(Mn2+)] reaches 20, the combustion of acetic acid under the same conditions is less than 1%, but excessive bromine will cause equipment stress corrosion. Since the acetic acid combustion loss is a major loss in the production of PTA and the combustion of acetic acid must be controlled, it is very important to control the n(Br-)/[n(Co2+)+n(Mn2+)] ratio in the reactor. Since the catalyst recovery system uses oxalic acid to precipitate cobalt and manganese ions, the Br- ions in the mother liquor are discharged along with the liquid phase to the stripper until they are used as a residue discharge device. Therefore, when the catalyst recovery system is put into use online, in order to maintain the n(Br-)/[n(Co2+)+n(Mn2+)] ratio in the system within the required range, the fresh bromide consumption will increase.
4. Economic comparison
The yield of PTA of Jiangsu Yizheng Chemical Fiber Co., Ltd. is 450,000 t/a. The consumption of fresh catalyst before and after the catalyst recovery system is put into use is shown in Table 1.
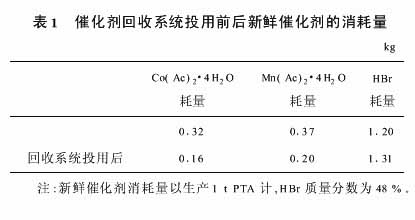
The current price of cobalt acetate is 160 yuan/kg, and the current price of manganese acetate is 15 yuan/kg. Excluding equipment maintenance and parking caustic washing costs, it can save about 8 million yuan annually, and the economic benefit is considerable. The investment cost can be recovered within 2 years after being put into use.
5 Conclusion
(1) The PTA residue is precipitated using a recovery reagent, and then cobalt acetate and manganese acetate are recovered by centrifugation to recover approximately 90% of cobalt ions and approximately 75% of manganese ions. In the recovery process, cobalt acetate, manganese acetate and oxalic acid form cobalt oxalate and manganese oxalate precipitates, and then return to the paraxylene oxidation reactor to participate in the reaction. However, the mechanism of cobalt oxalate and manganese oxalate participating in the reaction at high temperature is not yet known. No relevant report was found.
(2) In the recovery system, oxalic acid and free bromide ions are very important for corrosion of the equipment, so it is necessary to control the amount of oxalic acid and alkali added. However, to prevent corrosion of the equipment, it is also necessary to balance the Na+ ion concentration in the reactor.
(3) There is no emission of exhaust gas in the process of catalyst recovery, no pollution to the environment, reducing the content of metal ions in the residue, greatly reducing the pollution of the residue to the environment, and having good social benefits. At the same time, due to the recovery of precious metal cobalt, the use of fresh precious metal cobalt is reduced by about 50%, which greatly reduces the production cost of the PTA plant.
Explore Nails,Golden French False Nail,24Pcs Press On Nail,Long Coffin Flase Nails,Mix Color Coffin False Nails
Zhong Shan Senboma Artware Co.,Ltd , https://www.senbomanails.com
![<?echo $_SERVER['SERVER_NAME'];?>](/template/twentyseventeen/skin/images/header.jpg)