1 Introduction
Nitrogen is one of the large amount of nutrients necessary for plant growth and development. Nitrogen contributes 40% to 50% of the final crop yield, but excessive application of nitrogen will also bring serious negative effects. In recent years, due to the excessive application of nitrogen fertilizer and unreasonable management measures in agricultural production, a large amount of nitrogen cannot be absorbed by the crops of the season and enriched in the soil. Due to soil nitrification, NO3-N leaching and denitrification caused N2O, The loss of NO and the loss of ammonia volatilization leads to potential threats such as soil acidification, groundwater nitrate pollution, eutrophication of rivers and lakes, and atmospheric environmental pollution; in addition, it can also cause nitrogen stress in plants to exceed the critical value and form nitrogen stress , Directly affect the absorption and utilization of water and light energy by plants. According to statistics, the current annual application of nitrogen fertilizer in China is 25 million tons, which is three times the world average, but the utilization efficiency of nitrogen fertilizer is only 30%. Therefore, it is of great significance to extensively carry out research in the fields of reducing the pollution risk of nitrogen application to the environment such as water and soil, improving nitrogen utilization rate, and ensuring the safety of agricultural products.
2 Observation system design
2.1 Objective
In previous traditional studies, the nitrogen content of plants was measured indoors by collecting samples. Soil nitrification and denitrification are usually measured by taking back soil samples or applying exogenous isotopes and inhibitors. The leaching of soil NO3-N is also taken in the field. Experimental soil column, simulation research in the laboratory. These processes have destroyed the original structure of the sample and changed its inherent growth environment conditions, which cannot accurately reflect the true situation; and the traditional test methods require a lot of manpower and material resources in sampling, measurement and data analysis. , Poor timeliness.
The AZ-A202 in situ nitrogen migration observation system takes plants, soil and groundwater continuum as objects for systematic observation, provides scientific means for elucidating the transformation and migration law of nitrogen in plants, soil and groundwater, and provides scientific fertilization management and Improve nitrogen utilization efficiency and provide data support.
The AZ-A202 in situ nitrogen migration observation system uses a chlorophyll measurement unit based on spectral analysis technology to test live samples in the field quickly, in situ, and non-destructively to measure the nitrogen content of plants; a nitrogen stress measurement unit is used to measure ultraviolet and blue light excitation Infrared fluorescence ratio, effective diagnosis of plant nitrogen nutrition stress level; adopts the soil nitrogen conversion rate measurement unit based on international advanced method pressure process separation (BaPS) technology, taking undisturbed soil samples as the object, and simultaneously measuring a certain soil temperature and soil The total soil nitrification rate and denitrification rate under water conditions, so as to quantitatively analyze the dominant microbiological process (nitrification or denitrification) in the soil under different environmental conditions, to judge soil nitrification and denitrification under excessive fertilization Contribution rate to groundwater nitrate pollution and air pollution; using in situ soil solution sampling units buried at different depths of field soil, combined with an automatic soil ion analysis unit, to monitor the downward leaching and migration of nitrogen in real time under conditions close to nature Process and conduct long-term positioning tests.
2.2 Sample collection
2.2.1 Soil sample collection
Under natural conditions, a representative typical area is selected as the sampling plot; under experimental research conditions, a specific area is selected as the sampling plot according to the purpose of the study. According to the conditions of plot type, openness and flatness, soil homogeneity and other conditions, "plum blossom", "checkerboard", "S" and "grid method" can be selected for layout. For the same type of soil samples, take 3 to 7 undisturbed soils This is repeated. The time and frequency of sample collection are determined according to the research object and purpose. For specific operations and details, please refer to the relevant sections in Soil Physical and Chemical Analysis.
2.2.2 Soil solution sampling
In farmland soil, soil solution samplers are usually buried in the following layers, 0-20cm, 20-40cm, 40-60cm, 60-80cm, 80-100cm, 100-150cm. The sampling frequency is usually at least once every 2 weeks in the growing season, and the frequency is lower in the non-growing season.
2.3 Observation indicators
Relative plant chlorophyll content, ratio of infrared fluorescence excited by ultraviolet light and blue light, total soil nitrification rate, soil denitrification rate, NO3-N concentration.
2.4 Composition of the observation system
The AZA202 in situ nitrogen migration observation system consists of a plant chlorophyll content measurement unit, a plant nitrogen nutrient stress measurement unit, a soil nitrogen conversion rate measurement unit, a soil nitrogen leaching migration observation unit, a groundwater sampling unit, and a soil ion automatic analysis unit. composition.
3 Data processing
3.1 Relative chlorophyll content (CCI)-reflects the nitrogen content of plants
CCI = 931nm transmittance% / 653nm transmittance%
3.2 Soil nitrogen conversion rate-reflecting the contribution of nitrification and denitrification in soil to groundwater and air pollution
The soil nitrogen conversion rate measurement unit of this system mainly focuses on three soil microbiological processes in soil respiration, nitrification, and denitrification, and monitors O2 consumption (â–³ O2), CO2 production (â–³ CO2), and the total change of gas ( â–³ n).
Soil respiration process: CH2O + O2? CO2 + H2O
Heterotrophic nitrifying bacteria nitrification process: NH4 + + 2O2? NO3- + H2O + H +
Autotrophic nitrifying bacteria nitrification process: NH3 + 1.68O2 + 0.23CO2? 0.05C5H7O2N + 0.86H2O + 0.95HNO3
Denitrification process: 5CH2O + 4NO3- + 4H +? 5CO2 + 7H2O + 2NxOy
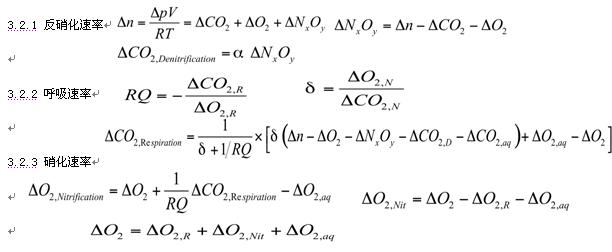
4 Application case
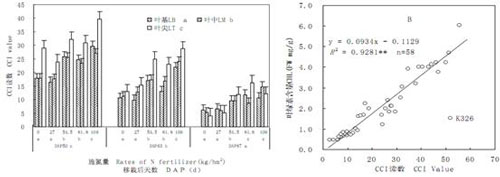
4.1 Using the relative chlorophyll content measurement unit to judge the nitrogen nutrition status of tobacco (Li Fulin et al., 2007)
The relative chlorophyll content, actual chlorophyll concentration, and total nitrogen concentration of flue-cured tobacco leaves in different nitrogen application rates and flue-cured tobacco varieties were measured during the growing season from 2003 to 2005, and the relationship between the three was analyzed. The results show that the best measurement site for flue-cured tobacco leaves using the chlorophyll relative content measurement unit is the middle of the fully unfolded leaves. The measured value of the relative chlorophyll content measurement unit varies with the year, location, nitrogen fertilizer level, leaf position, and different parts of the same leaf. There is a stable and extremely significant correlation between the reading of the relative chlorophyll content measurement unit and the total nitrogen concentration of the leaves. The regression equation between the reading of the relative chlorophyll content measurement unit and the total nitrogen content is N = 0.0265SPAD + 0.9601 (R2 = 0.7649, p <0.001). The tested model has good accuracy and universality. It is feasible for the unit to monitor flue-cured tobacco nitrogen nutrition.
4.2 Soil nitrogen conversion rate measurement unit applied to soil nitrification-denitrification and respiration under drip irrigation in the desert oasis zone (Bu Dongsheng, Zheng Deming et al., 2009)
The nitrification-denitrification rate and respiration rate of mulched and bare soil (CK) soils under conventional fertilization and non-fertilization conditions were studied by using air pressure process separation (BaPS) method. The law of respiration. The results showed that the nitrification-denitrification rate and respiration rate of the film-covered and bare soil under two fertilization levels had obvious seasonal changes; the nitrification-denitrification rate and respiration rate of the two different cultivation measures of the film-covered and bare soil The difference is extremely significant. Under the same cultivation measures, the nitrification-denitrification and respiration rate between different fertilization treatments also reached a very significant level; the nitrification-denitrification rate and respiration rate were ranked as follows under different cultivation measures and different fertilization levels: Membrane> bare ground, conventional fertilization> no fertilization. It can be seen that agricultural cultivation measures and different fertilization levels on soil nitrification-denitrification and respiration.
Stainless Steel Non-Welding Bucket
Stainless Steel Non-Welding Bucket,Commercial Stainless Steel Stock Pot,Commercial Cooking Pot,Commercial Cookware Stockpot
Jiangmen Vanky Stainless Steel Products Co., Ltd. , https://www.vankystar.com
![<?echo $_SERVER['SERVER_NAME'];?>](/template/twentyseventeen/skin/images/header.jpg)