The distribution and differentiation of photosynthesis and respiration in the net ecosystem carbon exchange (NEE) is challenging, and it is often associated with the generation of an unknown number of uncertainties, which hinders the development of the model. This is related to the equations and methods we use to measure NEE. Although there are many ways to distinguish between NEE, these techniques are often not implemented at the same time, making each method uniquely difficult to assess.
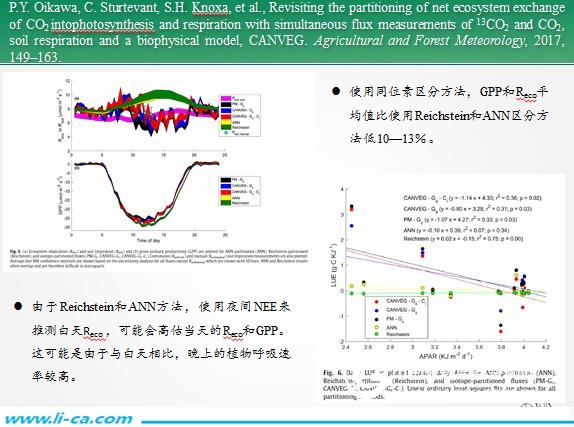
This study proposes the use of multiple distinguishing methods (Reichstein method, artificial neural network (ANN) method, stable carbon isotope method and soil respiration Rsoil method) under ideal conditions to establish a nonlinear regression model analysis. The flux of the steady-state C isotope of the ecosystem was measured by a new quantum cascade laser (QCL) spectrometer, which was matched to the physical model CANVEG and solved for total primary productivity (GPP) and ecosystem respiration (Reco). The results show that the GPP and Reco averages using the isotope discrimination method are 10-13% lower than the Reichstein and ANN discrimination methods. These results indicate that due to the Reichstein and ANN methods, the use of nighttime NEE to speculate during the daytime Reco may overestimate the day's Reco and GPP. This is because the plant respiration rate is higher in the evening than in the daytime, otherwise it is called the Kok effect.
As isotope measurement methods and applied theory continue to evolve in different ecosystems, it will not only be a benchmark measurement technology, but also have a certain significance for further understanding of the carbon cycle. Future research on assessing the application of these technologies in increasingly complex ecosystems will continue to increase the use of these studies to determine the differences between differentiation methods and how these differences affect the establishment of terrestrial carbon budget models.
[Source]
PY Oikawa, C. Sturtevant, SH Knoxa, et al., Revisiting the partitioning of net ecosystem exchange of CO2 into photosynthesis and respiration with simultaneous flux measurements of 13CO2 and CO2, soil respiration and a biophysical model, CANVEG.Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 2017 , 149–163.
Zhejiang Lamon Technology Inc. , https://www.babychaires.com
![<?echo $_SERVER['SERVER_NAME'];?>](/template/twentyseventeen/skin/images/header.jpg)